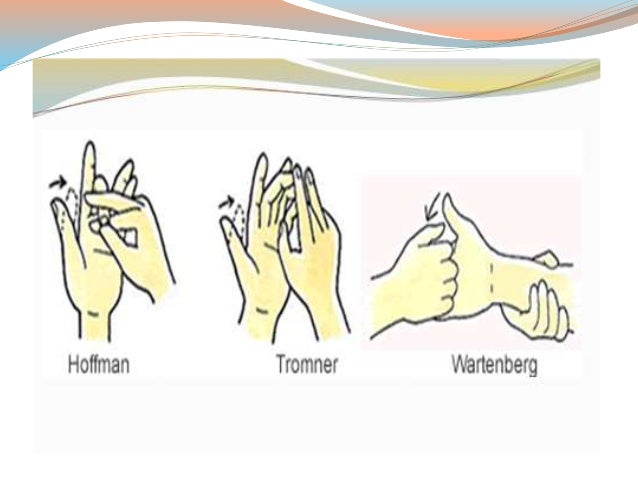
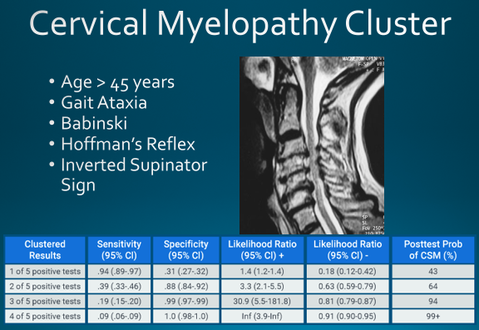
Cervical stenosis with myelopathy can have symptoms similar to several other conditions, such as multiple sclerosis (MS) or vitamin B12 deficiency, among others 1 It is important to get an accurate diagnosis before starting treatment Diagnosing cervical stenosis with myelopathy usually begins with a detailed medical history of the patient and a physical exam in the doctor's officeJun 12, 18 · According to the Indian Journal of Medical Specialties, the Hoffman sign is more likely to occur in people with cervical myelopathy or injuries or damage to the cervical spine, which is the upperFigure 3 Hoffmann sign

Cervical Myelopathy Spine Orthobullets
What is myelopathy cervical
What is myelopathy cervical-Note, however, that In one study involving 43 patients with cervical myelopathy, CSC correlated poorly with findings on the neurologic examination In this study, 16% of patients had clonus, 44% had a positive Romberg sign, 60% had an abnormal gait, and 67% had a positive Hoffman sign 1Study design Systematic review Objective To determine the validity of the Hoffmann sign for the detection of degenerative cervical myelopathy (DCM) for patients presenting with cervical complaints Summary of background data While physical examination maneuvers are often used to diagnose DCM, no previous review has synthesized diagnostic accuracy data




Axial Neck Pain Radiculopathy And Myelopathy Recognition And Treatment
Hoffmann Sign Red Flag for Cervical Myelopathy The Hoffmann sign is used by examiners assessing patients with symptoms of myelopathy (spinal cord compression) The test is done by quickly snapping or flicking the patient's middle fingernailIn patients surgically treated for cervical myelopathy, the Hoffmann sign is more prevalent and more likely to be seen in individuals with less severe neurological deficits than the Babinski sign In patients with lumbar symptoms, a bilateral Hoffmann sign was aFeb 21, 13 · One of our jobs as physical therapist's include identifying red flags and ruling out more serious disorders that warrant referring out Considering I treat a great deal of spinal patients (especially ones of increasing age), one disorder that comes to mind is identifying cervical spine myelopathy (CSM) The main concern with this condition is the
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us CreatorsSep 25, 17 · The Hoffman sign may indicate a condition that affects the cervical spinal cord, but it may happen even if you don't have any spinal conditions TheMyelopathy can be subdivided on the basis of upper or lower motor neurone injury The usual complaints are unsteady/clumsy gait, altered sensation, bowel and bladder dysfunction (in the late stages), lower extremity spasticity and diffuse hyperreflexia with the possible presence of the Babinski, sign, Hoffman reflexes, or any
Feb 17, 21 · The gold standard for diagnosing cervical myelopathy is an MRI A 15 study found that positive cord signal changes seen on MRI correlate with 67% of those with Hoffman sign The Hoffman sign is not always indicative of pathological cord compression But when it is present with corresponding MRI images, it was shown that if the compression ofMar 01, 07 · The dynamic Hoffman is thought to correlate with a narrowed cervical canal and is felt to be an earlier clinical indicator of cervical spondylotic myelopathy than a typical Hoffman sign 29 Download Download highres image (769KB) Download Download fullsize image;Oct 30, 18 · HOFFMANN'S SIGN OR REFLEX FOR CERVICAL SPONDYLOTIC MYELOPATHY (CSM) Next to fractures, another red flag we have to screen for in the cervical spine is cervical spondylotic myelopathy (CSM), which is an encroachment of the spinal cord at cervical level by degenerative changes (uncinate process and facet joint osteophytosis, ossification or




Cervical Radiculopathy And Myelopathy Wayne Cheng Md Instructor




Detection Of Cerebral Reorganization Associated With Degenerative Cervical Myelopathy Using Diffusion Spectral Imaging Dsi Sciencedirect
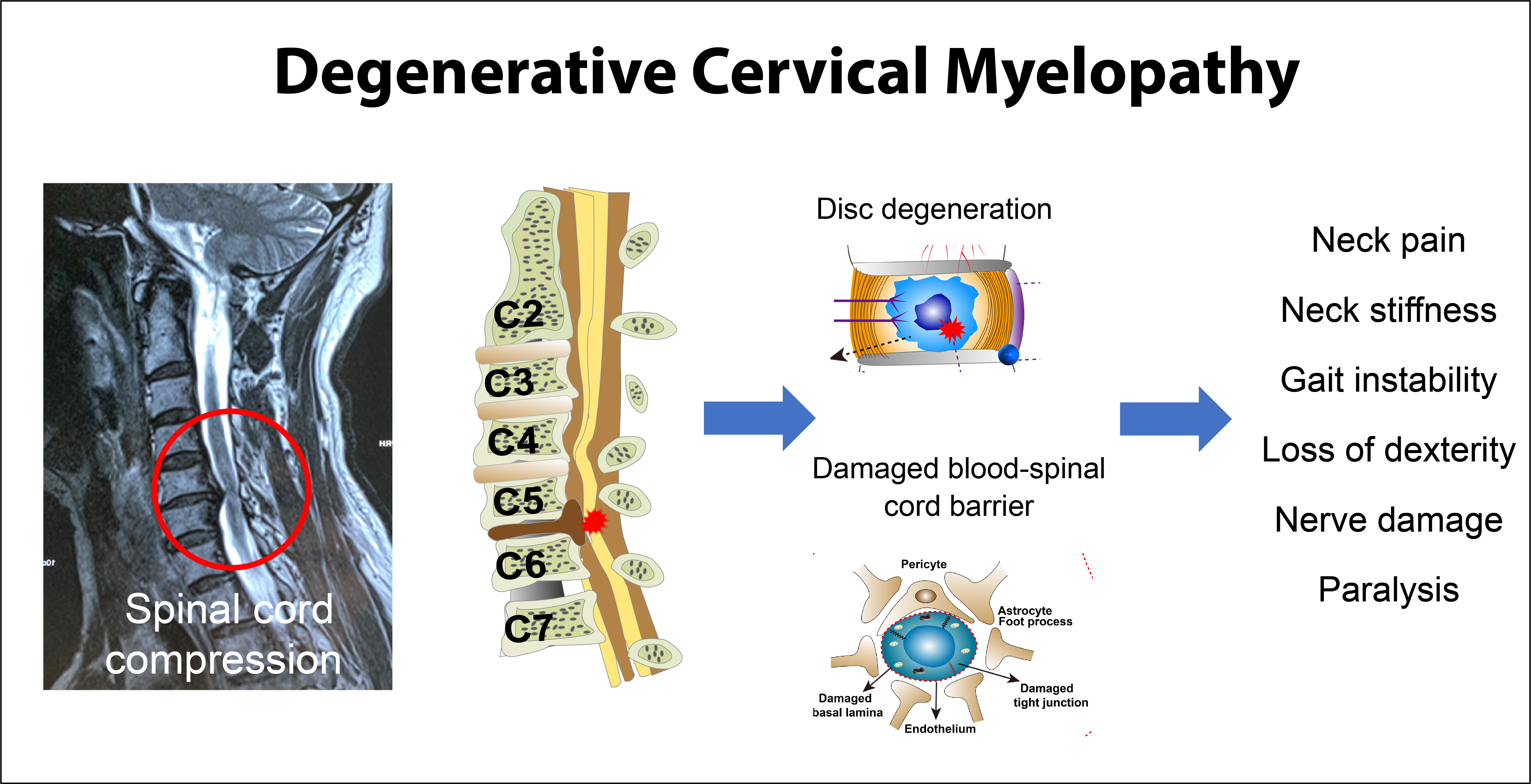
Sep 01, 08 · The Hoffmann sign is commonly used in clinical practice to assess cervical spine disease It is whether the sign correlates with the severity of myelopathy, and no consensus exists regarding the significance a positive sign in asymptomatic individualsMyelopathy describes any neurologic deficit related to the spinal cord When due to trauma, it is known as (acute) spinal cord injuryWhen inflammatory, it is known as myelitisDisease that is vascular in nature is known as vascular myelopathyThe most common form of myelopathy in humans, cervical spondylotic myelopathy (CSM), is caused by arthritic changes (spondylosis) of the cervicalMar 01, · Cervical spondylotic myelopathy (CSM) is the most common form of spinal cord injury in adults, accounting for 54% of nontraumatic spinal cord injury in North America 1 ⇓– 3 Cervical spondylosis is a progressive disease defined by degenerative changes affecting the vertebrae, intervertebral disks, facets, and associated ligaments




Cervical Myelopathy Spine Orthobullets




Degenerative Cervical Myelopathy The College Of Family Physicians Of Canada
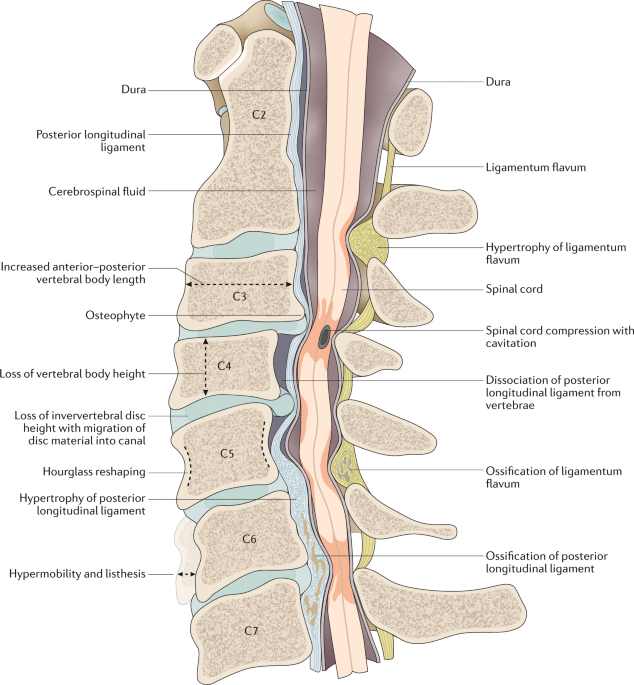
Patient with cervical myelopathy demonstrating Hoffman's and inverted brachioradialis reflex Cord compression seen as evidenced by effacement of cerebrospinHoffmann Sign is considered as a Red Flag for Cervical Myelopathy The Hoffmann sign is a reliable way to test for early signs of cervical myelopathy The presence of Hoffmann sign on both sides strongly suggests the presence of spinal cord compression in the cervical spine False positive and false negative Hoffman reflexClonus, Babinski, inverted radial reflex, Hoffman sign Search for Similar Articles You may search for similar articles that contain these same keywords or you may modify the keyword list to augment your search



Myelopathy Spinal Cord Compression Signs Symptoms
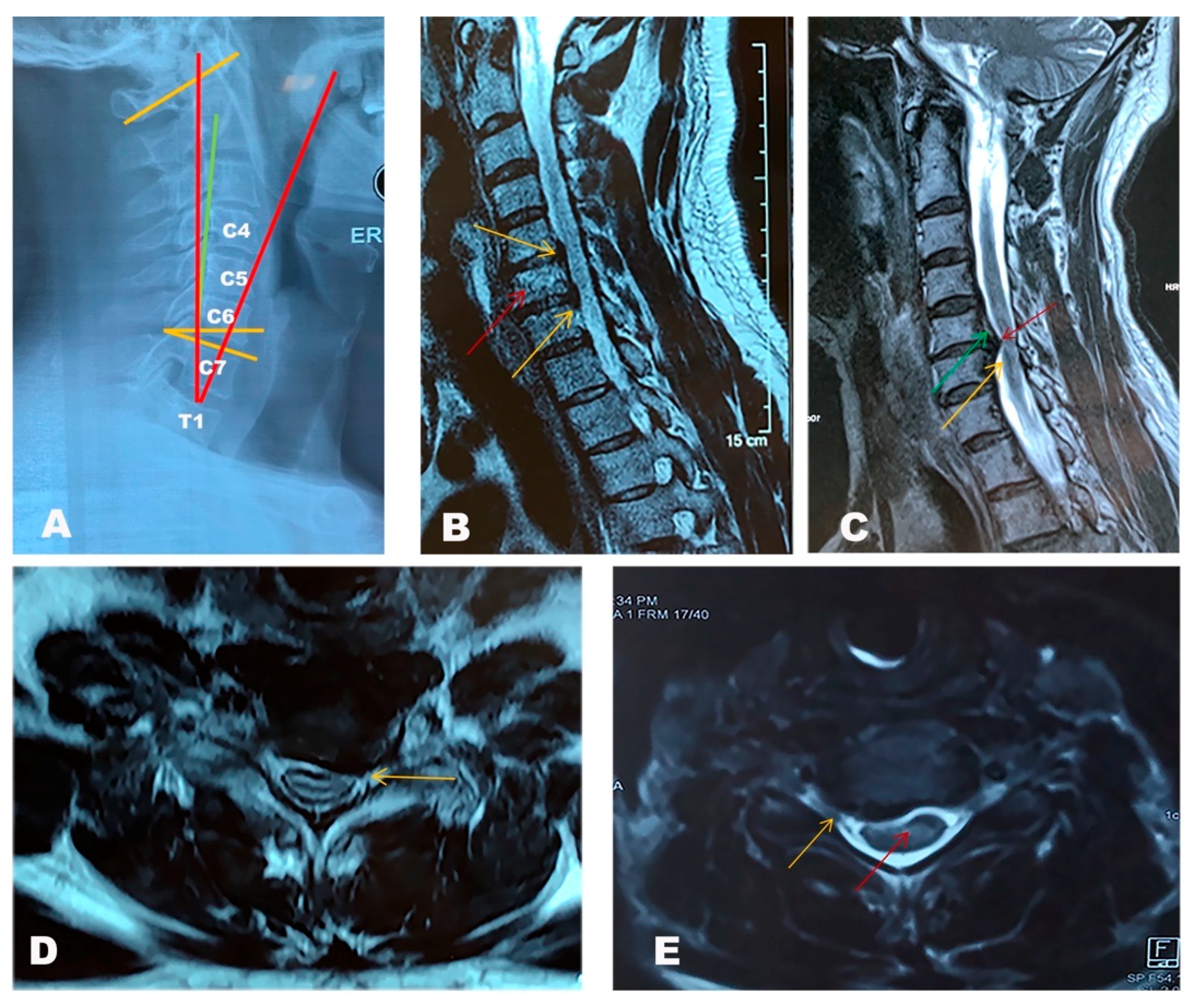



Jcm Free Full Text Degenerative Cervical Myelopathy Insights Into Its Pathobiology And Molecular Mechanisms Html
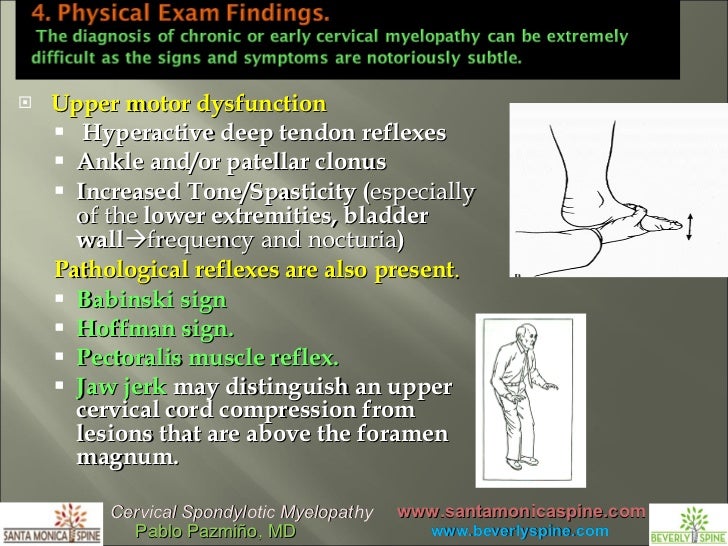
Apr 28, · In cervical spondylotic myelopathy, the most typical examination findings are suggestive of upper motor dysfunction, including hyperactive deep tendon reflexes, ankle and/or patellar clonusA Hoffman test is performed by flicking the fingernail of the long finger, from dorsal to volar, on each hand while the hand was supported by the examiner's hand The test was done with the neck in the neutral position and then with the neck maximally forward flexedDescription cervical myelopathy is a common degenerative condition caused by compression on the spinal cord that is characterized by clumsiness in hands and gait imbalance treatment is typically operative as the condition is progressive




Hoffmann S Sign Test Myelopathy Multiple Sclerosis




Different Presentations Of Myelopathy A Case Series Touchneurology
Feb 22, 18 · Degenerative cervical myelopathy (DCM), earlier referred to as cervical spondylotic myelopathy, involves spinal cord dysfunction from compression in the neck1 Patients report neurological symptoms such as pain and numbness in limbs, poor coordination, imbalance, and bladder problems o Hoffman's sign (thumb adduction/flexion /− fingerMar 04, 15 · The magnitude of mJOA improvement after surgery was comparable We conclude that diabetes may alter the typical signs and symptoms of cervical spondylotic myelopathy and suggest that knowledge of the differences may aid in securing a prompt and accurate diagnosisUpper extremity hyporeflexia (lower cervical lesion) or hyperreflexia (upper cervical lesion with a positive Hoffman sign) and intrinsic muscular atrophy Differential Diagnosis The differential diagnosis of cervical spondylotic myelopathy is quite broad




A Case Report Of Cervical Myelopathy After Neck Manipulation In A Patient With Cervical Spondylosis And Radiculopathy Cause And Effect Or Natural Progression Chauhan G Patri M Mordis Cj Loomba V




Positive Hoffman S Sign And Hyperreflexia With Cervical Spinal Stenosis Youtube
TABLE II Clinical Presentation of Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy Common symptoms Clumsy or weak hands Leg weakness or stiffness Neck stiffness Pain in shoulders or arms Unsteady gait Common signs Weakness of the hand musculature Hyperreflexia Lhermitte sign (electric shocklike sensation down the center of the back following flexion of theThe Hoffmann sign is commonly used in clinical practice to assess cervical spine disease It is unknown whether the sign correlates with the severity of myelopathy, and no consensus exists regarding the significance of a positive sign in asymptomatic individualsHoffman's sign was positive in the left upper extremity ncbinlmnihgov see exam of spinal cord presentation ( Bertalanffy, et al ) 61% presented with radicular symptoms 16% had pure myelopathic symptoms 23% had a combination of myelopathic and radiculopathy upper motor neuron findings such as hyperreflexia, clonus




Cervical Spondylosis Active Care Physiotherapy Clinic




Cervical Myelopathy Spine Orthobullets
Jan 01, 18 · Other eponymous upper motor neurone signs such as Hoffmann's test have been reported to have a low sensitivity 5 Weakness can be difficult to detect but clonus (more than 3 beats) is highly suggestive of cervical myelopathy Romberg's test may be positive, especially in more severe cases the patient become unbalanced when standing withA positive Hoffman's reflex may indicate an upper motor neuron lesion or a pyramidal sign Hoffmann's reflex may be seen in the following conditions Multiple sclerosis ALS Diseases which cause spinal cord compression (myelopathy) such as cervical spondylitis, tumors, or degenerative arthritisJul 01, 15 · Several clinical signs have been used as markers of cervical myelopathy – these include exaggerated deep tendon reflexes, Hoffman's reflex, the Babinski sign, increased tone, clonus, etc The Trömner and the Wazir hand myelopathy signs have also found to be very sensitive for detecting myelopathy at or above the C56 level 15




Cervical Deformity And Myelopathy In An Elderly Female
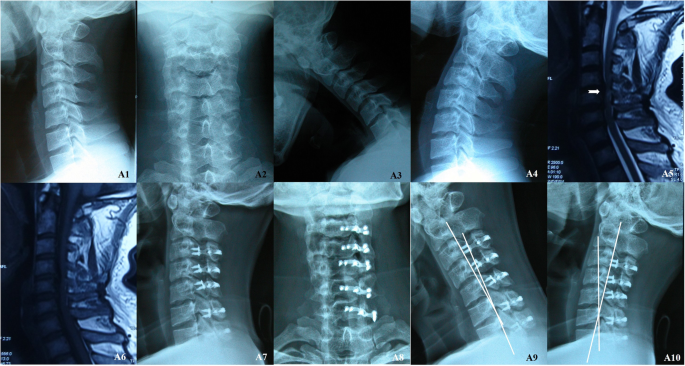



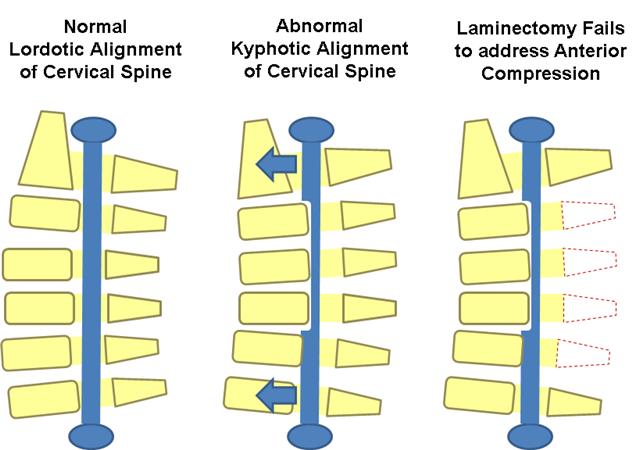
Is Laminectomy And Fusion The Better Choice Than Laminoplasty For Multilevel Cervical Myelopathy With Signal Changes On Magnetic Resonance Imaging A Comparison Of Two Posterior Surgeries Bmc Musculoskeletal Disorders Full Text
Aug 13, 15 · Various studies have opined that a positive Hoffmann Sign highly correlates to the presence of cervical myelopathy It is accepted knowledge that a positive Hoffmann response can also indicate the presence of Central Nervous System (Brain) abnormalities, asHoffmann's reflex (Hoffmann's sign, sometimes simply "Hoffmann's", also finger flexor reflex) is a neurological examination finding elicited by a reflex test which can help verify the presence or absence of issues arising from the corticospinal tractIt is named after neurologist Johann Hoffmann Usually considered a pathological reflex in a clinical setting, the Hoffmann's reflexApr , 09 · cervical myelopathy, physical signs, myelopathic signs, long tract signs, hyperreflexia;




Brasil Degenerative Cervical Myelopathy A Review Of Current Concepts Degenerative Cervical Myelopathy A Review Of Current Concepts Scielo
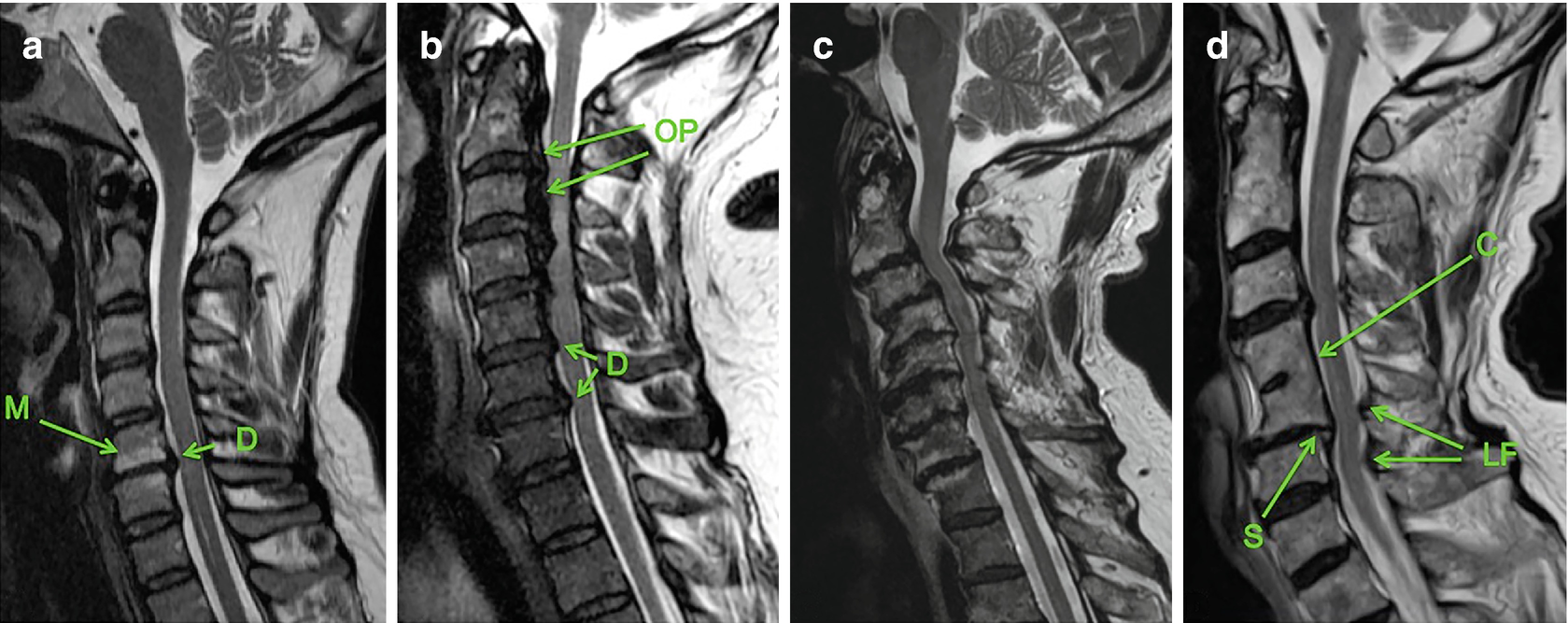



Degenerative Cervical Myelopathy A Spectrum Of Degenerative Spondylopathies Springerlink
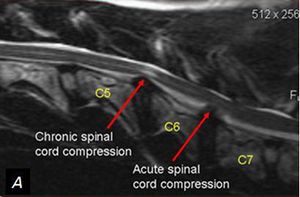
Apr 14, 17 · In patients with disease in the lumbar spine, but without cervical spine related symptoms, this sign is an indicator of a hidden compression in the cervical spine However, in a study by Glaser, Cura, Bailey and Morrow (01), who analyzed 165 patients with cervical spinal cord compression, they concluded that the Hoffman test is not a reliableNegative predictive value was 60%, 85%, 59%, and 38% for Hoffmann sign, Trömner sign, inverted radial reflex, and Babinski sign, respectively There were 63%–71% of patients in either axial pain group or cervical spondylotic radiculopathy group had positive Trömner sign Most of CSM patients with cord signal changed had positive myelopathicCervical myelopathy is insidious, because unlike compressed nerves radiating from the spinal cord, the spinal cord feels no pain and it is difficult for patients to say when the symptoms begin Cervical myelopathy is developed slowly, resulting from a spinal canal stenosis, which is a narrowing of the spinal canal It is the slow degeneration of the spine called spondylosis, which




Cervical Myelopathy And Cervical Radiculopathy Everything You Need To Know Dr Nabil Ebraheim Youtube




Cervical Myelopathy
Hoffman's Sign definition Hoffman's sign can be a feature of myelopathy involving the cervical spinal cord It is a test performed by doctors during their neurological examinationCervical myelopathy is a form of myelopathy that involves compression of the spinal cord in the cervical spine (neck) Your cervical spine contains seven vertebrae (C1 to C7), with six intervertebral discs and eight nerve roots The spinal cord travels inside the vertebral column constructed from the front by vertebrae, cushioned by theJun 28, · Hoffmann's sign is a test for pathological disorder in upper motor neuron reflex as seen in cervical myelopathy when the spinal cord in the cervical spine gets compressed and chances are that the patient will exhibit pathological reflexes The Hoffmann's sign is also known as a digital reflex, snapping reflex, Jacobson sign and trauma sign



Assessment Of Degenerative Cervical Myelopathy Differs Between Specialists And May Influence Time To Diagnosis And Clinical Outcomes




Clinical Correlations Of Cervical Myelopathy And The Hoffmann Sign In Journal Of Neurosurgery Spine Volume 9 Issue 3 08
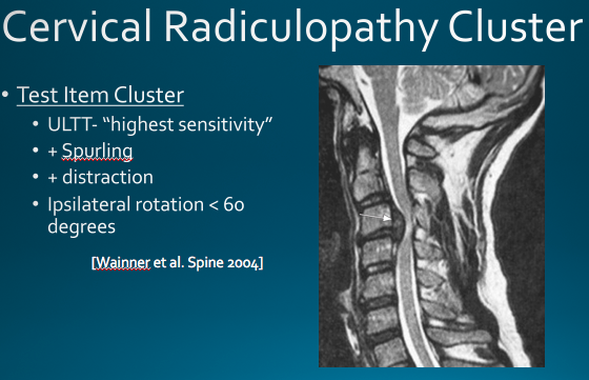
This is a retrospective study of 67 patients, seen during a 4year period, with cervical pathology requiring surgical correction The purpose of this study was to evaluate the usefulness of a new physical finding (dynamic Hoffmann's sign) in diagnosing early cervical myelopathy or in suggesting a narrow cervical canal clinicallyHoffmann Sign More Prevalent Than Babinski Sign in Less Severe Neurological Deficits from Cervical Myelopathy Doctors have different techniques for assessing the neurological, or nerve, function in your body For example, when an infant is being examined during a wellbaby checkup, one thing that is performed is the Babinski sign or reflexJul 01, 15 · Hoffmann sign Positive Babinski sign and/or clonus OR Progressive neurological deficit (motor deficit, bowel or bladder dysfunction) with evidence of Cervical radiculopathy or myelopathy from ruptured disc, spondylosis, spinal instability, or deformity Persistent or recurrent symptoms/pain with functional limitations that are unresponsive to



Cervical Myelopathy Spine Orthobullets



Cervical Myelopathy The Bone School




Cervical Radiculopathy Myelopathy University Hospitals




Pdf Cervical Myelopathy In Klippel Feil Syndrome




Hoffman S Sign What Do Positive And Negative Test Results Mean



Neurological Signs In Medicine




Hoffmann S Sign Postgraduate Medical Journal
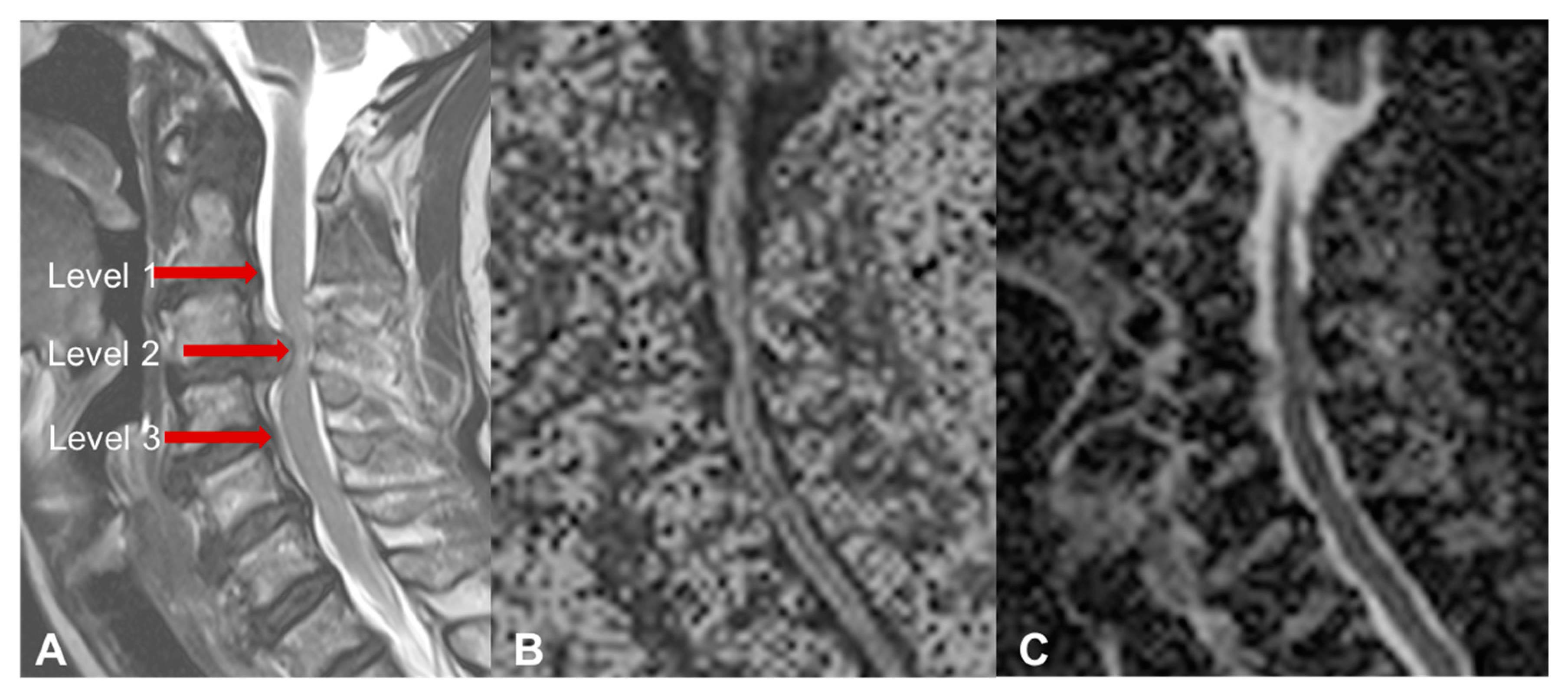



Jcm Free Full Text Degenerative Cervical Myelopathy How To Identify The Best Responders To Surgery Html




The Spine Clinics Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy Clinical Scenarios Nanda A Renjith K R Mallepally A Prasath C S Shetty Ap Indian Spine J




Axial Neck Pain Radiculopathy And Myelopathy Recognition And Treatment



Cervical Myelopathy Physiopedia




Cervical Radiculopathy Myelopathy University Hospitals




Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy A Common Cause Of Spinal Cord Dysfunction In Older Persons American Family Physician



Degenerative Cervical Myelopathy Natural History Clinical Presentation Current Diagnosis And Treatment Update Maeda International Journal Of Orthopaedics




Neck Pain Treatment Of Cervical Spine Pain Ppt Download




Dynamic Changes In The Reflex Exam Of Patients With Sub Axial Cervical Stenosis Journal Of Clinical Neuroscience




Effect Of Exercise Program On The Rehabilitation Of Patients With Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy
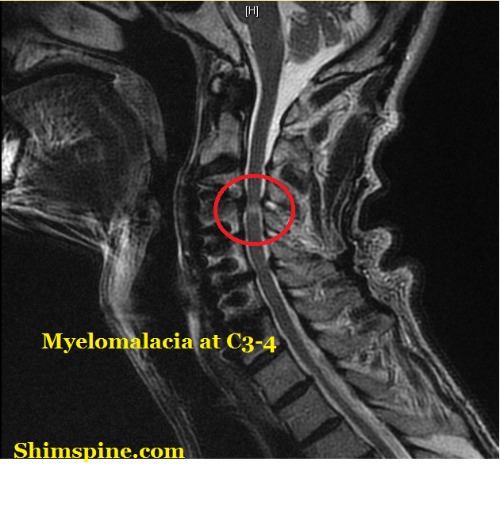



Hoffmann Sign And Myelopathy Shimspine




An Evaluation Of The Finger Flexion Hoffman S And Plantar Reflexes As Markers Of Cervical Spinal Cord Compression A Comparative Clinical Study Sciencedirect




Approaching Neck Pain Mcp Ipa Lbp Task Force Ppt Download




Clinical Correlations Of Cervical Myelopathy And The Hoffmann Sign In Journal Of Neurosurgery Spine Volume 9 Issue 3 08




Cervical Arthritis Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy By Pablo Pazmino
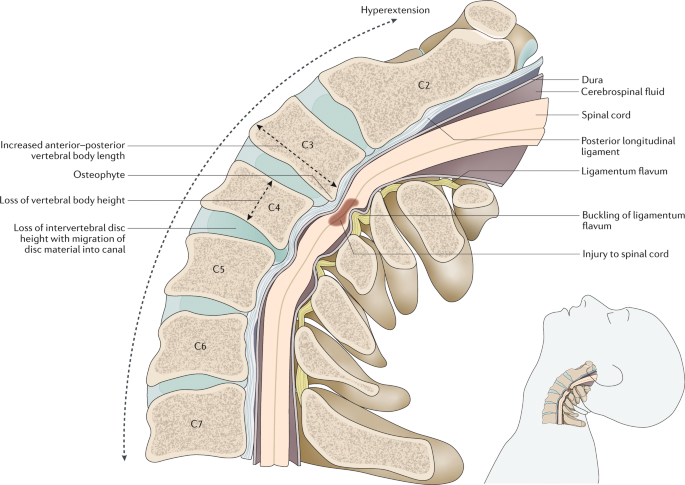



Degenerative Cervical Myelopathy Update And Future Directions Nature Reviews Neurology




Degenerative Cervical Spondylosis Nejm




Multiple Myeloma Cervical Spine Myelopathy Kyphotic Deformity
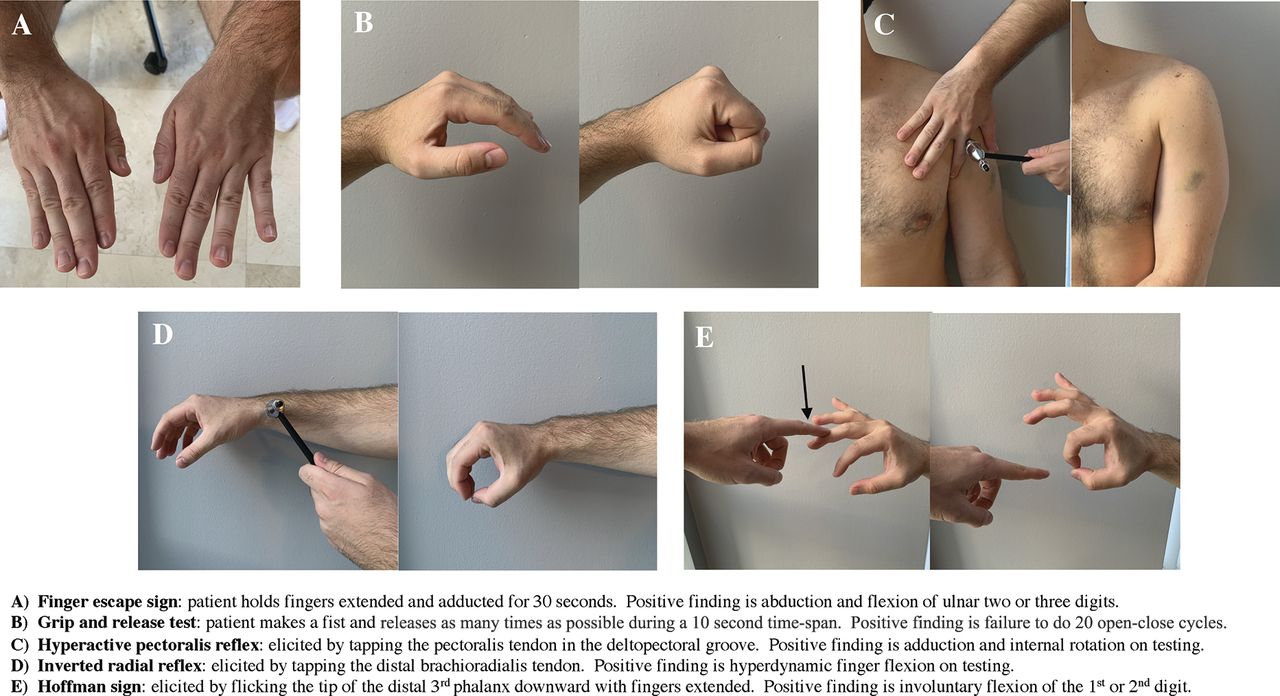



Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy A Guide To Diagnosis And Management American Board Of Family Medicine
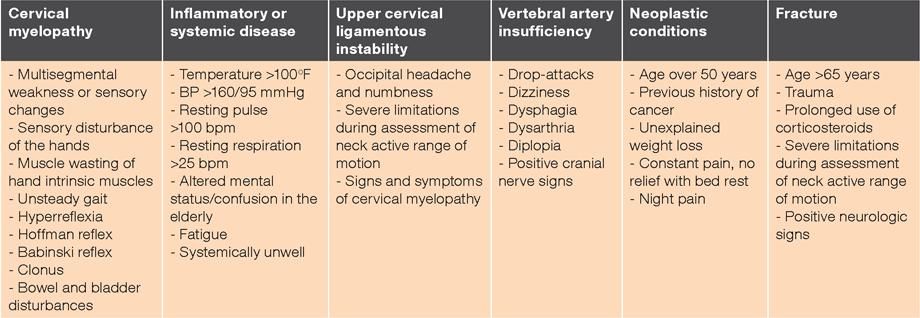



Csiro Publishing Journal Of Primary Health Care




Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy A Common Cause Of Spinal Cord Dysfunction In Older Persons American Family Physician




Axial Neck Pain Radiculopathy And Myelopathy Recognition And Treatment Page 3




Degenerative Cervical Myelopathy The Bmj




Primary Care Management Of The Degenerative Spine Jim




Time Is Brain Time Is Testicle Time Is Spine Brown Emergency Medicine




Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy A Common Cause Of Spinal Cord Dysfunction In Older Persons American Family Physician




Hoffmann S Sign Or Reflex Upper Motor Neuron Lesion Youtube




Cervical Myelopathy Johns Hopkins Medicine



Degenerative Cervical Myelopathy Update And Future Directions Nature Reviews Neurology



Blog Posts




Hoffman Sign Myelopathy What Does A Positive Or Negative Hoffman Sign Mean




Pdf Clinical Sign Revisited Hoffman S Sign



Jcm Free Full Text Degenerative Cervical Myelopathy Insights Into Its Pathobiology And Molecular Mechanisms Html




Current Diagnosis And Management Of Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy Abstract Europe Pmc



Degenerative Cervical Myelopathy Natural History Clinical Presentation Current Diagnosis And Treatment Update Maeda International Journal Of Orthopaedics



Cervical Myelopathy Everything You Need To Know Dr Nabil Ebraheim Youtube




Hoffmann Sign Article




Clinical Correlations Of Cervical Myelopathy And The Hoffmann Sign In Journal Of Neurosurgery Spine Volume 9 Issue 3 08




Nw Surgical Research Foundation Conference Ppt Download




Multilevel Critical Stenosis With Minimal Functional Deficits A Case Of Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy Spinal Cord Series And Cases




Ns Neurospine




Primary Care Management Of The Degenerative Spine Jim




Spinal Stenosis Chronic Fatigue Syndrome Me Cfs And Fibromyalgia The Spinal Series 3 Health Rising




Table 1 From Clinical Evidence For Cervical Myelopathy Due To Chiari Malformation And Spinal Stenosis In A Non Randomized Group Of Patients With The Diagnosis Of Fibromyalgia Semantic Scholar




Utility Of Extension Views In Spondylotic Myelopathy Mimicking Transverse Myelitis Multiple Sclerosis And Related Disorders




Degenerative Cervical Myelopathy The College Of Family Physicians Of Canada




Axial Neck Pain Radiculopathy And Myelopathy Recognition And Treatment Page 3




Clinical Spectrum And Importance Of Evaluation Systems In Degenerative Cervical Myeloradiculopathy Swaminathan G Muralidharan V Joseph Bv Indian Spine J



Cervical Spine Examination Orthopaedicprinciples Com



Cervical Arthritis Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy By Pablo Pazmino




C Spine T Spine And Cranial N Special Tests Flashcards Quizlet




Clinical Correlations Of Cervical Myelopathy And The Hoffmann Sign In Journal Of Neurosurgery Spine Volume 9 Issue 3 08



Blog Posts




Cervical Radiculopathy Myelopathy University Hospitals




Cervical And Lumbar Degeneration Flashcards Quizlet



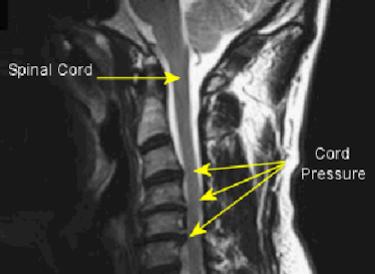
Cervical Myelopathy Hoffman Sign




Cervical Myelopathy




Medicosnotes Com What Is Hoffman Reflex A Complete Guide




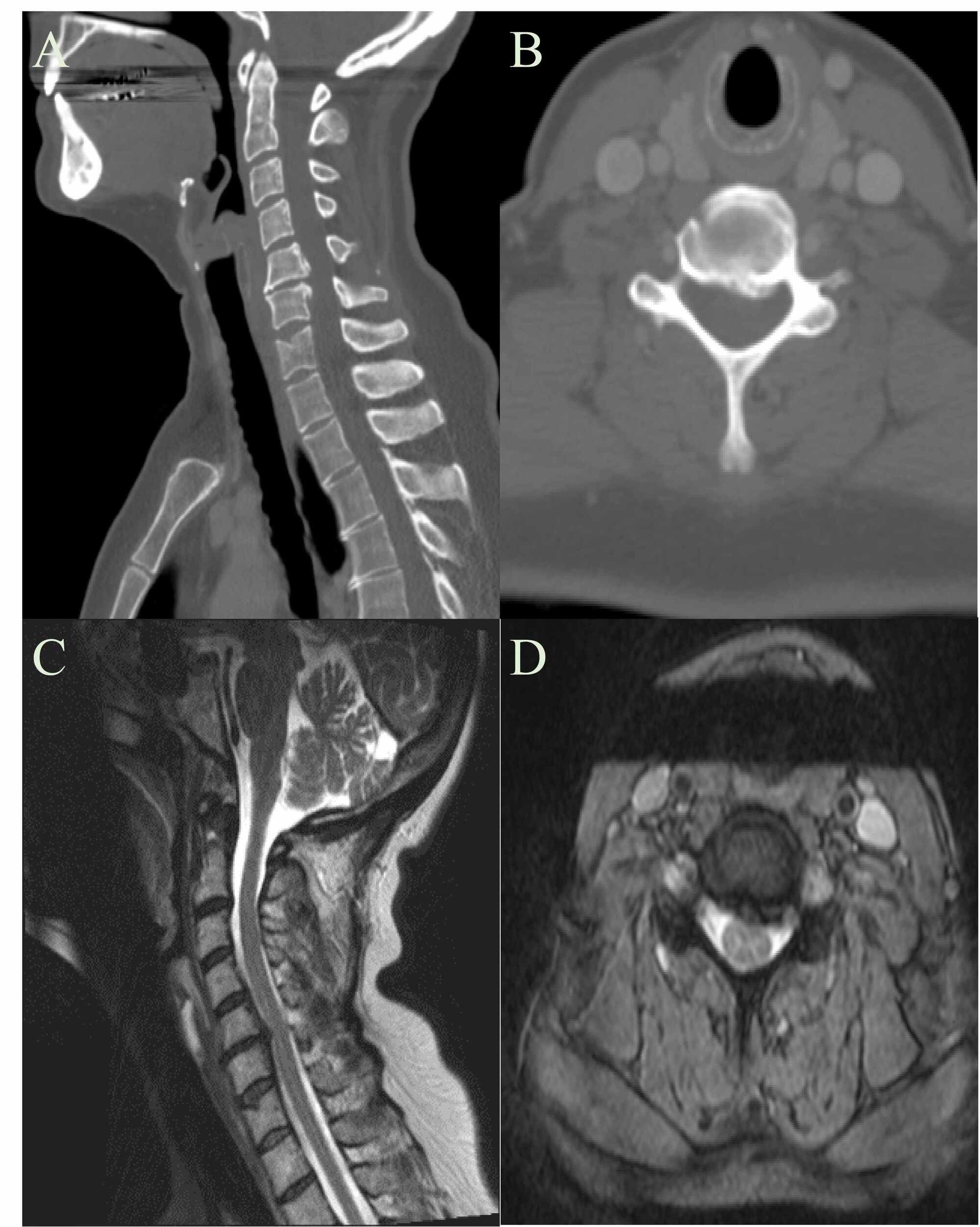
Congenital Malformed Posterior Arch Of Atlas With Fusion Defect A Case Of Developmental Canal Stenosis Causing Cervical Myelopathy Shah Journal Of Spine Surgery




Presence Of Undiagnosed Cervical Myelopathy In Patients Referred For Surgical Evaluation Of Lumbar Stenosis Semantic Scholar



Cervical Myelopathy Physiopedia



Cureus A Retrospective Pilot Study For Preoperative Screening To Prevent Iatrogenic Cervical Spinal Cord Injury




Cervical And Lumbar Degeneration Flashcards Quizlet



Myelopathy Physiopedia




Hoffman S Sign Definition Myelopathy Org




Lil Bone Peep Hoffmann S Sign Upper Motor Neuron Test Perform By Flicking Or Tapping The Nail While Relaxed Sign If The Thumb Index Finger Reflexively Adduct Flex




Key Signs And Symptoms Associated With Serious Pathological Neck Download Table


